
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
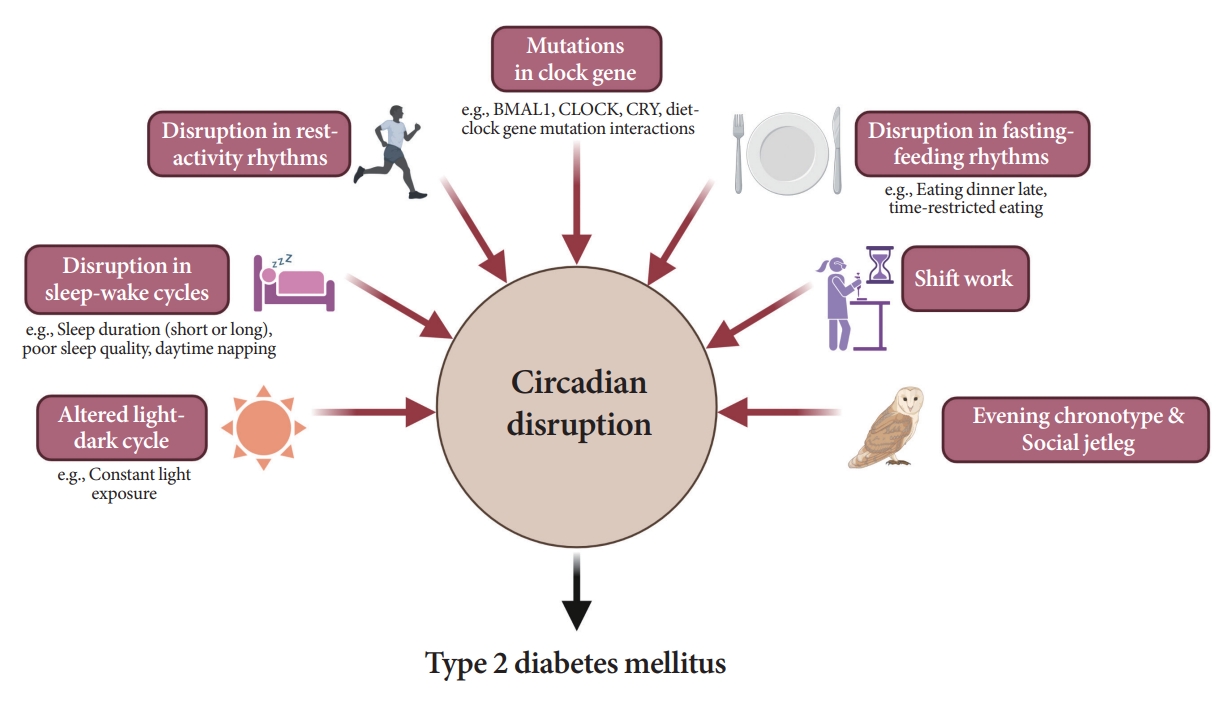
- Pathophysiology
- Attention to Innate Circadian Rhythm and the Impact of Its Disruption on Diabetes
- Da Young Lee, Inha Jung, So Young Park, Ji Hee Yu, Ji A Seo, Kyeong Jin Kim, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Sin Gon Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Nan Hee Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(1):37-52. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0193
- 2,153 View
- 219 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Novel strategies are required to reduce the risk of developing diabetes and/or clinical outcomes and complications of diabetes. In this regard, the role of the circadian system may be a potential candidate for the prevention of diabetes. We reviewed evidence from animal, clinical, and epidemiological studies linking the circadian system to various aspects of the pathophysiology and clinical outcomes of diabetes. The circadian clock governs genetic, metabolic, hormonal, and behavioral signals in anticipation of cyclic 24-hour events through interactions between a “central clock” in the suprachiasmatic nucleus and “peripheral clocks” in the whole body. Currently, circadian rhythmicity in humans can be subjectively or objectively assessed by measuring melatonin and glucocorticoid levels, core body temperature, peripheral blood, oral mucosa, hair follicles, rest-activity cycles, sleep diaries, and circadian chronotypes. In this review, we summarized various circadian misalignments, such as altered light-dark, sleep-wake, rest-activity, fasting-feeding, shift work, evening chronotype, and social jetlag, as well as mutations in clock genes that could contribute to the development of diabetes and poor glycemic status in patients with diabetes. Targeting critical components of the circadian system could deliver potential candidates for the treatment and prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus in the future.
- Technology/Device
- Clinical and Lifestyle Determinants of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Metrics in Insulin-Treated Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Da Young Lee, Namho Kim, Inha Jung, So Young Park, Ji Hee Yu, Ji A Seo, Jihee Kim, Kyeong Jin Kim, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Sin Gon Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Sung-Min Park, Nan Hee Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):826-836. Published online August 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0273

- 1,784 View
- 191 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
There was limited evidence to evaluate the association between lifestyle habits and continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) metrics. Thus, we aimed to depict the behavioral and metabolic determinants of CGM metrics in insulin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
This is a prospective observational study. We analyzed data from 122 insulin-treated patients with T2DM. Participants wore Dexcom G6 and Fitbit, and diet information was identified for 10 days. Multivariate-adjusted logistic regression analysis was performed for the simultaneous achievement of CGM-based targets, defined by the percentage of time in terms of hyper, hypoglycemia and glycemic variability (GV). Intake of macronutrients and fiber, step counts, sleep, postprandial C-peptide-to-glucose ratio (PCGR), information about glucose lowering medications and metabolic factors were added to the analyses. Additionally, we evaluated the impact of the distribution of energy and macronutrient during a day, and snack consumption on CGM metrics.
Results
Logistic regression analysis revealed that female, participants with high PCGR, low glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and daytime step count had a higher probability of achieving all targets based on CGM (odds ratios [95% confidence intervals] which were 0.24 [0.09 to 0.65], 1.34 [1.03 to 1.25], 0.95 [0.9 to 0.99], and 1.15 [1.03 to 1.29], respectively). And participants who ate snacks showed a shorter period of hyperglycemia and less GV compared to those without.
Conclusion
We confirmed that residual insulin secretion, daytime step count, HbA1c, and women were the most relevant determinants of adequate glycemic control in insulin-treated patients with T2DM. In addition, individuals with snack consumption were exposed to lower times of hyperglycemia and GV. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Explanatory variables of objectively measured 24-h movement behaviors in people with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review
Lotte Bogaert, Iris Willems, Patrick Calders, Eveline Dirinck, Manon Kinaupenne, Marga Decraene, Bruno Lapauw, Boyd Strumane, Margot Van Daele, Vera Verbestel, Marieke De Craemer
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2024; 18(4): 102995. CrossRef
- Explanatory variables of objectively measured 24-h movement behaviors in people with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review
- Others
- Fasting Glucose Variability and the Risk of Dementia in Individuals with Diabetes: A Nationwide Cohort Study
- Da Young Lee, Jaeyoung Kim, Sanghyun Park, So Young Park, Ji Hee Yu, Ji A Seo, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Sin Gon Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyungdo Han, Nan Hee Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(6):923-935. Published online May 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0346
- 5,602 View
- 254 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We investigated whether fasting glucose (FG) variability could predict the risk of dementia.
Methods
This cohort study analyzed data from Koreans with diabetes after at least three health examinations by the Korean National Health Insurance Corporation between 2005 and 2010, which included at least one examination between 2009 and 2010. A total of 769,554 individuals were included, excluding those aged <40 years and those with dementia. FG variability was measured using the variability independent of the mean (FG-VIM). The incidence of dementia was defined by the International Classification of Diseases 10th Revision codes and prescription of anti-dementia medication and was subdivided into Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and vascular dementia (VD).
Results
During the 6.9-year follow-up, 54,837, 41,032, and 6,892 cases of all-cause dementia, AD, and VD, respectively, were identified. Cox proportional regression analyses showed that as the FG-VIM quartile increased, the risk of dementia serially increased after adjustment for metabolic factors, income status, and diabetes-related characteristics, including the mean FG. Participants in FG-VIM quartile 4 showed a 18%, 19%, and 17% higher risk for all-cause dementia, AD, and VD, respectively, than those in quartile 1; this particularly included non-obese patients with a longer duration of diabetes, high FG levels, dyslipidemia, and those taking glucose-lowering medications. Conversely, the baseline FG status and dementia showed a U-shaped association.
Conclusion
Increased FG variability over 5 years can predict the risk of dementia in individuals with diabetes in Korea. This finding was more pronounced in patients with less favorable metabolic profiles. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fasting glucose variability and risk of dementia in Parkinson’s disease: a 9-year longitudinal follow-up study of a nationwide cohort
Sung Hoon Kang, Yunjin Choi, Su Jin Chung, Seok-Joo Moon, Chi Kyung Kim, Ji Hyun Kim, Kyungmi Oh, Joon Shik Yoon, Sang Won Seo, Geum Joon Cho, Seong-Beom Koh
Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a Diabetic Microenvironment on Neurodegeneration: Special Focus on Neurological Cells
Vishal Chavda, Dhananjay Yadav, Snehal Patel, Minseok Song
Brain Sciences.2024; 14(3): 284. CrossRef - The Association of Glucose Variability and Dementia Incidence in Latinx Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Study
Heather Cuevas, Elizabeth Muñoz, Divya Nagireddy, Jeeyeon Kim, Grace Ganucheau, Fathia Alomoush
Clinical Nursing Research.2023; 32(2): 249. CrossRef - The effects of long-term cumulative HbA1c exposure on the development and onset time of dementia in the patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Hospital based retrospective study (2005–2021)
Sunyoung Cho, Choon Ok Kim, Bong-soo Cha, Eosu Kim, Chung Mo Nam, Min-Gul Kim, Min Soo Park
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 201: 110721. CrossRef - Physiological Mechanisms Inherent to Diabetes Involved in the Development of Dementia: Alzheimer’s Disease
Himan Mohamed-Mohamed, Victoria García-Morales, Encarnación María Sánchez Lara, Anabel González-Acedo, Teresa Pardo-Moreno, María Isabel Tovar-Gálvez, Lucía Melguizo-Rodríguez, Juan José Ramos-Rodríguez
Neurology International.2023; 15(4): 1253. CrossRef - Cumulative effect of impaired fasting glucose on the risk of dementia in middle-aged and elderly people: a nationwide cohort study
Jin Yu, Kyu-Na Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Fasting glucose variability and risk of dementia in Parkinson’s disease: a 9-year longitudinal follow-up study of a nationwide cohort
- Technology/Device
- Comparison of Laser and Conventional Lancing Devices for Blood Glucose Measurement Conformance and Patient Satisfaction in Diabetes Mellitus
- Jung A Kim, Min Jeong Park, Eyun Song, Eun Roh, So Young Park, Da Young Lee, Jaeyoung Kim, Ji Hee Yu, Ji A Seo, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Hye Jin Yoo, Nan Hee Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(6):936-940. Published online March 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0293
- 5,269 View
- 256 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Self-monitoring of capillary blood glucose is important for controlling diabetes. Recently, a laser lancing device (LMT-1000) that can collect capillary blood without skin puncture was developed. We enrolled 150 patients with type 1 or 2 diabetes mellitus. Blood sampling was performed on the same finger on each hand using the LMT-1000 or a conventional lancet. The primary outcome was correlation between glucose values using the LMT-1000 and that using a lancet. And we compared the pain and satisfaction of the procedures. The capillary blood sampling success rates with the LMT-1000 and lancet were 99.3% and 100%, respectively. There was a positive correlation (r=0.974, P<0.001) between mean blood glucose levels in the LMT-1000 (175.8±63.0 mg/dL) and conventional lancet samples (172.5±63.6 mg/dL). LMT-1000 reduced puncture pain by 75.0% and increased satisfaction by 80.0% compared to a lancet. We demonstrated considerable consistency in blood glucose measurements between samples from the LMT-1000 and a lancet, but improved satisfaction and clinically significant pain reduction were observed with the LMT-1000 compared to those with a lancet.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison between a laser-lancing device and automatic incision lancet for capillary blood sampling from the heel of newborn infants: a randomized feasibility trial
Chul Kyu Yun, Eui Kyung Choi, Hyung Jin Kim, Jaeyoung Kim, Byung Cheol Park, Kyuhee Park, Byung Min Choi
Journal of Perinatology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Comparison between a laser-lancing device and automatic incision lancet for capillary blood sampling from the heel of newborn infants: a randomized feasibility trial
- Variability of Metabolic Risk Factors: Causative Factor or Epiphenomenon?
- Hye Jin Yoo
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):257-259. Published online March 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0060
- 3,067 View
- 131 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between carotid atherosclerosis and presence of intracranial atherosclerosis using three-dimensional high-resolution vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic patients with type 2 diabetes
Ji Eun Jun, You-Cheol Hwang, Kyu Jeong Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung, Geon-Ho Jahng, Soonchan Park, In-Kyung Jeong, Chang-Woo Ryu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 191: 110067. CrossRef - Mean versus variability of lipid measurements over 6 years and incident cardiovascular events: More than a decade follow-up
Soroush Masrouri, Leila Cheraghi, Niloofar Deravi, Neda Cheraghloo, Maryam Tohidi, Fereidoun Azizi, Farzad Hadaegh
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association between carotid atherosclerosis and presence of intracranial atherosclerosis using three-dimensional high-resolution vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic patients with type 2 diabetes
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Myocardial Infarction, Stroke, and All-Cause Mortality according to Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level in the Elderly, a Nationwide Study
- You-Bin Lee, Minji Koo, Eunjin Noh, Soon Young Hwang, Jung A Kim, Eun Roh, So-hyeon Hong, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Geum Joon Cho, Hye Jin Yoo
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):722-732. Published online March 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0225
- 6,974 View
- 331 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We assessed the myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, and all-cause death risks during follow-up according to the low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels among older adults.
Methods
The Korean National Health Insurance Service datasets (2002 to 2020) were used for this population-based cohort study. The hazards of MI, stroke, and all-cause mortality during follow-up were analyzed according to LDL-C level in individuals aged ≥65 years without baseline cardiovascular diseases (n=1,391,616).
Results
During a mean 7.55 years, 52,753 MIs developed; 84,224 strokes occurred over a mean 7.47 years. After a mean 8.50 years, 233,963 died. A decrease in LDL-C was associated with lower hazards of MI and stroke. The decreased hazard of stroke in lower LDL-C was more pronounced in statin users, and individuals with diabetes or obesity. The hazard of all-cause death during follow-up showed an inverted J-shaped pattern according to the LDL-C levels. However, the paradoxically increased hazard of mortality during follow-up in lower LDL-C was attenuated in statin users and individuals with diabetes, hypertension, or obesity. In statin users, lower LDL-C was associated with a decreased hazard of mortality during follow-up.
Conclusion
Among the elderly, lower LDL-C was associated with decreased risks of MI and stroke. Lower LDL-C achieved by statins in the elderly was associated with a decreased risk of all-cause death during follow-up, suggesting that LDL-C paradox for the premature death risk in the elderly should not be applied to statin users. Intensive statin therapy should not be hesitated for older adults with cardiovascular risk factors including diabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Combination of low- or moderate-intensity statin and ezetimibe vs. high-intensity statin monotherapy on primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and all-cause death: a propensity-matched nationwide cohort study
Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Kyu Jeong Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung, You-Cheol Hwang
European Journal of Preventive Cardiology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations of Low-density Lipoprotein Cholesterol With All-cause and Cause-specific Mortality in Older Adults in China
Wenqing Ni, Yuebin Lv, Xueli Yuan, Yan Zhang, Hongmin Zhang, Yijing Zheng, Xiaoming Shi, Jian Xu
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and all-cause or cardiovascular mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes: a retrospective study
Chin-Huan Chang, Shu-Tin Yeh, Seng-Wei Ooi, Chung-Yi Li, Hua-Fen Chen
PeerJ.2023; 11: e14609. CrossRef - ERCC1 polymorphism and its expression associated with ischemic stroke in Chinese population
Xiao-Dong Deng, Jian-Lin Ke, Tai-Yu Chen, Qin Gao, Zhuo-Lin Zhao, Wei Zhang, Huan Liu, Ming-Liang Xiang, Li-Zhen Wang, Ying Ma, Yun Liu
Frontiers in Neurology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - New, Novel Lipid-Lowering Agents for Reducing Cardiovascular Risk: Beyond Statins
Kyuho Kim, Henry N. Ginsberg, Sung Hee Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 517. CrossRef - Association between the Diabetes Drug Cost and Cardiovascular Events and Death in Korea: A National Health Insurance Service Database Analysis
Seung Min Chung, Ji-In Lee, Eugene Han, Hyun-Ae Seo, Eonju Jeon, Hye Soon Kim, Ji Sung Yoon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(5): 759. CrossRef
- Combination of low- or moderate-intensity statin and ezetimibe vs. high-intensity statin monotherapy on primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and all-cause death: a propensity-matched nationwide cohort study
- Basic Research
- GPR40 Agonism Modulates Inflammatory Reactions in Vascular Endothelial Cells
- Joo Won Kim, Eun Roh, Kyung Mook Choi, Hye Jin Yoo, Hwan-Jin Hwang, Sei Hyun Baik
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):506-511. Published online January 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0092

- 4,726 View
- 229 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Endothelial dysfunction is strongly linked with inflammatory responses, which can impact cardiovascular disease. Recently, G protein-coupled receptor 40 (GPR40) has been investigated as a modulator of metabolic stress; however, the function of GPR40 in vascular endothelial cells has not been reported. We analyzed whether treatment of GPR40-specific agonists modulated the inflammatory responses in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Treatment with LY2922470, a GPR40 agonist, significantly reduced lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-mediated nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) phosphorylation and movement into the nucleus from the cytosol. However, treatment with another GPR40 agonist, TAK875, did not inhibit LPS-induced NF-κB activation. LPS treatment induced expression of adhesion molecules vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and attachment of THP-1 cells to HUVECs, which were all decreased by LY2922470 but not TAK875. Our results showed that ligand-dependent agonism of GPR40 is a promising therapeutic target for overcoming inflammatory reactions in the endothelium.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthetic GPR40/FFAR1 agonists: An exhaustive survey on the most recent chemical classes and their structure-activity relationships
Abhik Paul, Sourin Nahar, Pankaj Nahata, Arnab Sarkar, Avik Maji, Ajeya Samanta, Sanmoy Karmakar, Tapan Kumar Maity
European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.2024; 264: 115990. CrossRef - Metabolite-sensing GPCRs in rheumatoid arthritis
Xuezhi Yang, Wankang Zhang, Luping Wang, Yingjie Zhao, Wei Wei
Trends in Pharmacological Sciences.2024; 45(2): 118. CrossRef - GPR40 deficiency worsens metabolic syndrome‐associated periodontitis in mice
Yanchun Li, Zhongyang Lu, Cameron L. Kirkwood, Keith L. Kirkwood, Stephen A. Wank, Ai‐Jun Li, Maria F. Lopes‐Virella, Yan Huang
Journal of Periodontal Research.2023; 58(3): 575. CrossRef - Signaling pathways and intervention for therapy of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Rong Cao, Huimin Tian, Yu Zhang, Geng Liu, Haixia Xu, Guocheng Rao, Yan Tian, Xianghui Fu
MedComm.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - G Protein-Coupled Receptor 40 Agonist LY2922470 Alleviates Ischemic-Stroke-Induced Acute Brain Injury and Functional Alterations in Mice
Yingyu Lu, Wanlu Zhou, Qinghua Cui, Chunmei Cui
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(15): 12244. CrossRef - AM1638, a GPR40-Full Agonist, Inhibited Palmitate- Induced ROS Production and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Enhancing HUVEC Viability in an NRF2-Dependent Manner
Hwan-Jin Hwang, Joo Won Kim, SukHwan Yun, Min Jeong Park, Eyun Song, Sooyeon Jang, Ahreum Jang, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Hye Jin Yoo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 760. CrossRef - Learn from failures and stay hopeful to GPR40, a GPCR target with robust efficacy, for therapy of metabolic disorders
Hong-Ping Guan, Yusheng Xiong
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Synthetic GPR40/FFAR1 agonists: An exhaustive survey on the most recent chemical classes and their structure-activity relationships
- Time to Reach Target Glycosylated Hemoglobin Is Associated with Long-Term Durable Glycemic Control and Risk of Diabetic Complications in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 6-Year Observational Study (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:368-78)
- Kyoung Jin Kim, Jimi Choi, Jae Hyun Bae, Kyeong Jin Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A Seo, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Sin Gon Kim, Nam Hoon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):617-618. Published online July 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0152
- 3,828 View
- 99 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of close and intensive therapeutic monitoring of patients with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes with different glycemic background
Ayşe Naciye Erbakan, Müzeyyen Arslan Bahadir, Fatoş Nimet Kaya, Büşra Güleç, Miraç Vural Keskinler, Özge Faydaliel, Banu Mesçi, Aytekin Oğuz
Medicine.2023; 102(50): e36680. CrossRef - Reduced macula microvascular densities may be an early indicator for diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Xiaoyu Deng, Shiqi Wang, Yan Yang, Aizhen Chen, Jinger Lu, Jinkui Hao, Yufei Wu, Qinkang Lu
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- The effect of close and intensive therapeutic monitoring of patients with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes with different glycemic background
- The Role of Adipose Tissue Lipolysis in Diet-Induced Obesity: Focus on Vimentin
- Eun Roh, Hye Jin Yoo
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(1):43-45. Published online January 22, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0293
- 3,957 View
- 142 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bioinformatics and Next-Generation Data Analysis for Identification of Genes and Molecular Pathways Involved in Subjects with Diabetes and Obesity
Prashanth Ganekal, Basavaraj Vastrad, Satish Kavatagimath, Chanabasayya Vastrad, Shivakumar Kotrashetti
Medicina.2023; 59(2): 309. CrossRef - Selegiline Modulates Lipid Metabolism by Activating AMPK Pathways of Epididymal White Adipose Tissues in HFD-Fed Obese Mice
Hye-Young Joung, Jung-Mi Oh, Min-Suk Song, Young-Bae Kwon, Sungkun Chun
Pharmaceutics.2023; 15(11): 2539. CrossRef - An analogue of the Prolactin Releasing Peptide reduces obesity and promotes adult neurogenesis
Sara KM Jörgensen, Alena Karnošová, Simone Mazzaferro, Oliver Rowley, Hsiao-Jou Cortina Chen, Sarah J Robbins, Sarah Christofides, Florian T Merkle, Lenka Maletínská, David Petrik
EMBO Reports.2023; 25(1): 351. CrossRef
- Bioinformatics and Next-Generation Data Analysis for Identification of Genes and Molecular Pathways Involved in Subjects with Diabetes and Obesity
- Complications
-
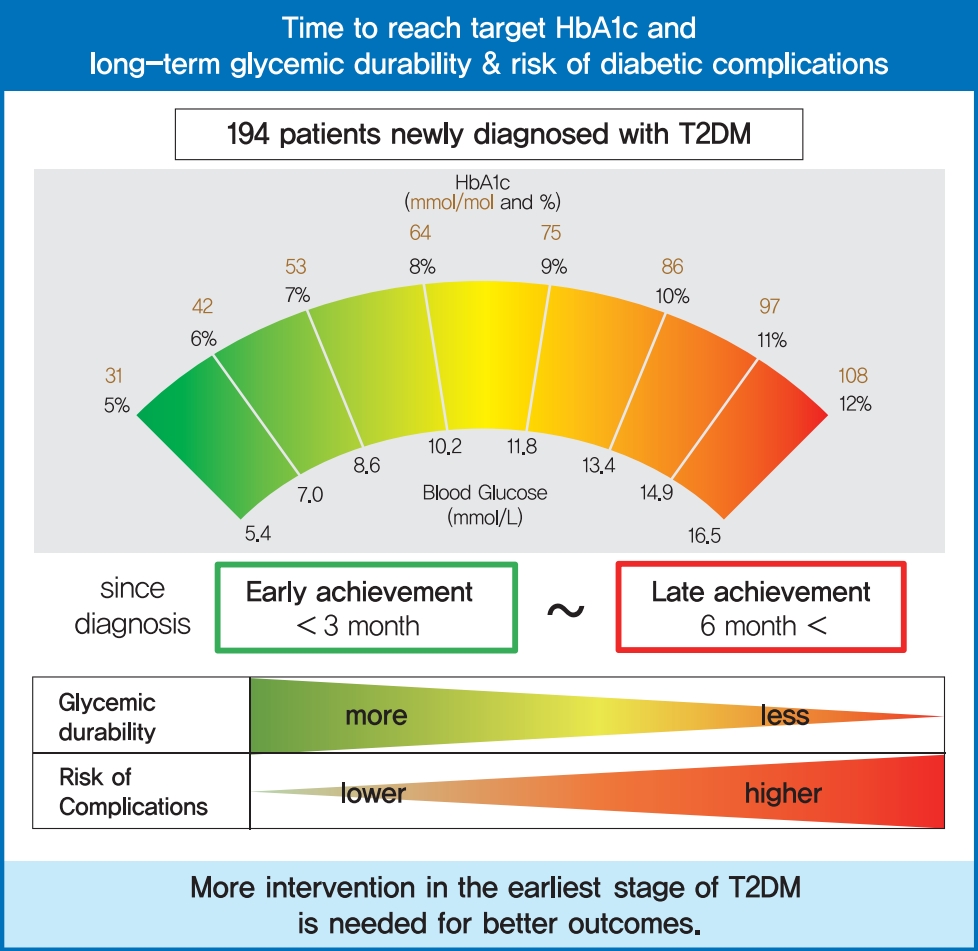
- Time to Reach Target Glycosylated Hemoglobin Is Associated with Long-Term Durable Glycemic Control and Risk of Diabetic Complications in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 6-Year Observational Study
- Kyoung Jin Kim, Jimi Choi, Jae Hyun Bae, Kyeong Jin Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A Seo, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Sin Gon Kim, Nam Hoon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(3):368-378. Published online October 20, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0046
- 9,376 View
- 343 Download
- 19 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
To evaluate the association of time to reach the target glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level with long-term durable glycemic control and risk of diabetic complications in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
In a longitudinal observational cohort, 194 patients with T2DM newly diagnosed between January 2011 and March 2013 were followed up over 6 years. Patients were classified according to the time needed to reach the target HbA1c (<7.0%): <3, 3 to 6 (early achievement group), and ≥6 months (late achievement group). Risks of microvascular complications including diabetic retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy as well as macrovascular events including ischemic heart disease, ischemic stroke, and peripheral arterial disease were assessed by multivariable Cox proportional hazards analysis.
Results
During a median follow-up of 6.53 years, 66 microvascular and 14 macrovascular events occurred. Maintenance of durable glycemic control over 6 years was more likely in the early achievement groups than in the late achievement group (34.5%, 30.0%, and 16.1% in <3, 3 to 6, and ≥6 months, respectively, P=0.039). Early target HbA1c achievement was associated with lower risk of composite diabetic complications (adjusted hazard ratio [HR, 0.47; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.26 to 0.86 in <3 months group) (adjusted HR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.23 to 1.10 in 3 to 6 months group, in reference to ≥6 months group). Similar trends were maintained for risks of microvascular and macrovascular complications, although statistical significance was not reached for macrovascular complications.
Conclusion
Early target HbA1c achievement was associated with long-term durable glycemic control and reduced risk of diabetic complications in newly diagnosed T2DM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- HbA1c As Diabetes Mellitus Biomarker and Its Methods Evolution
Liong Boy Kurniawan
INDONESIAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PATHOLOGY AND MEDICAL LABORATORY.2024; 30(2): 191. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin vs. dapagliflozin as add-on therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus based on renal function: a pooled analysis of two randomized controlled trials
Young Sang Lyu, Sangmo Hong, Si Eun Lee, Bo Young Cho, Cheol-Young Park
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of health quotient and time management skills on self-management behavior and glycemic control among individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Mengjie Chen, Man Liu, Ying Pu, Juan Wu, Mingjiao Zhang, Hongxia Tang, Laixi Kong, Maoting Guo, Kexue Zhu, Yuxiu Xie, Zhe Li, Bei Deng, Zhenzhen Xiong
Frontiers in Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycemic control and cardiovascular complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus
I. V. Druk, S. S. Safronova
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2023; (13): 130. CrossRef - Effect of viscous soluble dietary fiber on glucose and lipid metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis on randomized clinical trials
Kun Lu, Tingqing Yu, Xinyi Cao, Hui Xia, Shaokang Wang, Guiju Sun, Liang Chen, Wang Liao
Frontiers in Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Construction and validation of a clinical prediction model for asymptomatic obstructive coronary stenosis in patients with carotid stenosis
Cuijie Qin, Chuang Li, Yunpeng Luo, Zhen Li, Hui Cao
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk assessment of rectal anastomotic leakage (RAREAL) after DIXON in non-emergency patients with rectal cancer
Xue-Cong Zheng, Jin-Bo Su, Jin-Jie Zheng
BMC Gastroenterology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Left Ventricular Function in Diabetes Patients with Microvascular Disease by Three-Dimensional Speckle Tracking Imaging
青 周
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(12): 18908. CrossRef - Validity of the diagnosis of diabetic microvascular complications in Korean national health insurance claim data
Hyung Jun Kim, Moo-Seok Park, Jee-Eun Kim, Tae-Jin Song
Annals of Clinical Neurophysiology.2022; 24(1): 7. CrossRef - Metformin plus a low hypoglycemic risk antidiabetic drug vs. metformin monotherapy for untreated type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Wei-Tse Hung, Yuan-Jung Chen, Chun-Yu Cheng, Bruce Ovbiagele, Meng Lee, Chia-Yu Hsu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 189: 109937. CrossRef - Peripheral arterial disease progression and ankle brachial index: a cohort study with newly diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes
João Soares Felício, Franciane Trindade Cunha de Melo, Giovana Miranda Vieira, Vitória Teixeira de Aquino, Fernanda de Souza Parente, Wanderson Maia da Silva, Nivin Mazen Said, Emanuele Rocha da Silva, Ana Carolina Contente Braga de Souza, Maria Clara Ner
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of long-term visit-to-visit variability of HbA1c and fasting glycemia with hypoglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Chen Long, Yaling Tang, Jiangsheng Huang, Suo Liu, Zhenhua Xing
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Degree of Glycemic Control for the First Three Months Determines the Next Seven Years
Nami Lee, Dae Jung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Inhibition of advanced glycation end products and protein oxidation by leaf extracts and phenolics from Chilean bean landraces
Felipe Ávila, Nadia Cruz, Jazmin Alarcon-Espósito, Nélida Nina, Hernán Paillan, Katherine Márquez, Denis Fuentealba, Alberto Burgos-Edwards, Cristina Theoduloz, Carmina Vejar-Vivar, Guillermo Schmeda-Hirschmann
Journal of Functional Foods.2022; 98: 105270. CrossRef - Mediation Effect of Self-Efficacy Between Health Beliefs and Glycated Haemoglobin Levels in Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-Sectional Study
Anqi Zhang, Jinsong Wang, Xiaojuan Wan, Jing Zhang, Zihe Guo, Yamin Miao, Shuhan Zhao, Shuo Bai, Ziyi Zhang, Weiwei Yang
Patient Preference and Adherence.2022; Volume 16: 3015. CrossRef - Early Glycosylated Hemoglobin Target Achievement Predicts Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Joonyub Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(3): 337. CrossRef - Time to Reach Target Glycosylated Hemoglobin Is Associated with Long-Term Durable Glycemic Control and Risk of Diabetic Complications in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 6-Year Observational Study (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:368-78)
Ja Young Jeon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 613. CrossRef - Time to Reach Target Glycosylated Hemoglobin Is Associated with Long-Term Durable Glycemic Control and Risk of Diabetic Complications in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 6-Year Observational Study (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:368-78)
Kyoung Jin Kim, Jimi Choi, Jae Hyun Bae, Kyeong Jin Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A Seo, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Sin Gon Kim, Nam Hoon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 617. CrossRef - Plasma Nesfatin-1: Potential Predictor and Diagnostic Biomarker for Cognitive Dysfunction in T2DM Patient
Dandan Xu, Yue Yu, Yayun Xu, Jinfang Ge
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 3555. CrossRef
- HbA1c As Diabetes Mellitus Biomarker and Its Methods Evolution
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
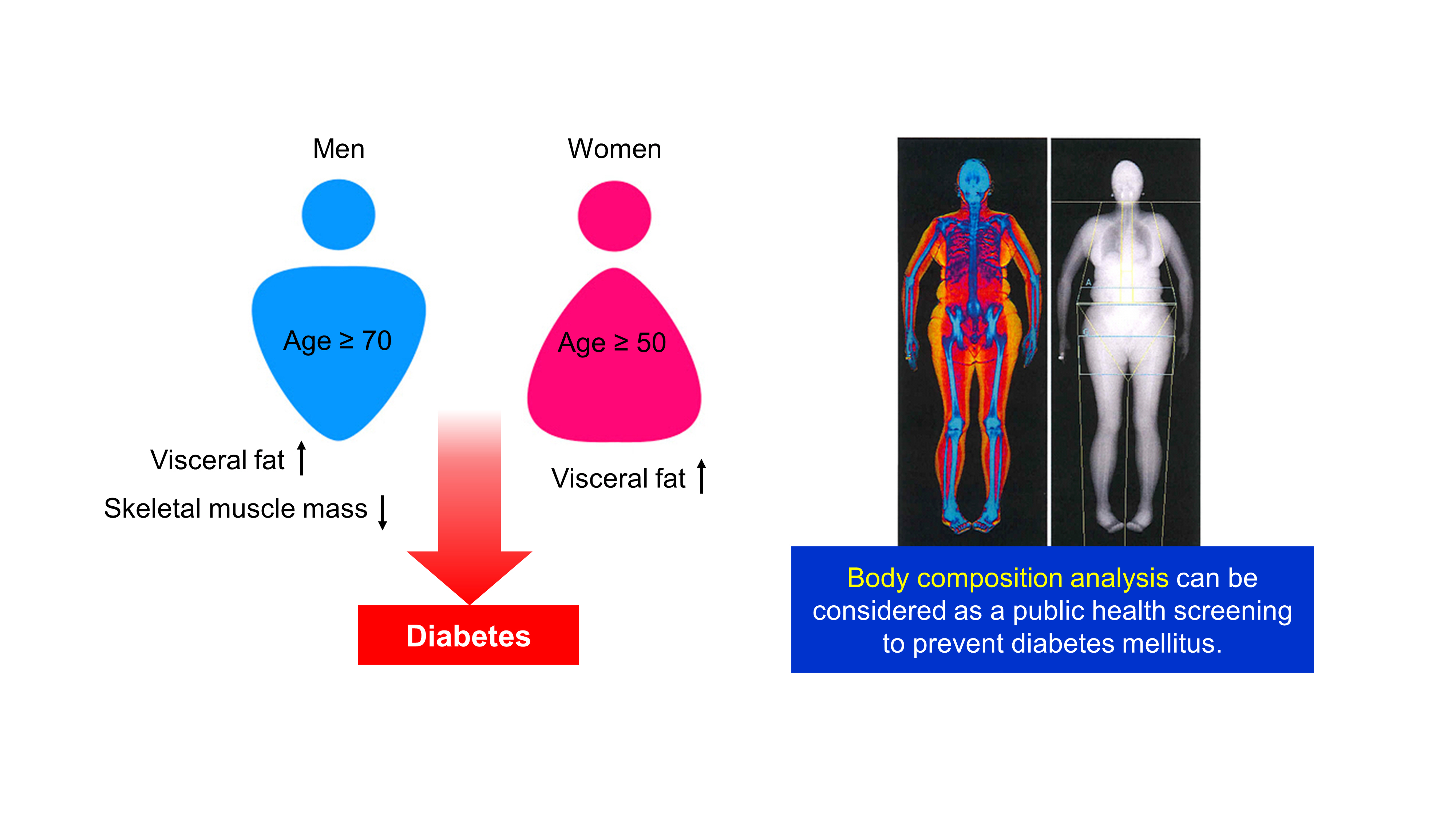
- Age- and Sex-Related Differential Associations between Body Composition and Diabetes Mellitus
- Eun Roh, Soon Young Hwang, Jung A Kim, You-Bin Lee, So-hyeon Hong, Nam Hoon Kim, Ji A Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Hye Jin Yoo
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(2):183-194. Published online June 16, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0171
- 7,431 View
- 236 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
Background The age- and sex-related differences on the impacts of body composition on diabetes mellitus (DM) remain uncertain.
Methods The fourth and fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey included 15,586 subjects over 30 years of age who completed dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. We conducted a cross-sectional study to investigate whether muscle mass index (MMI), defined as appendicular skeletal muscle divided by body mass index (BMI), and fat mass index (FMI), defined as trunk fat mass divided by BMI, were differently associated with DM according to age and sex.
Results In multivariate logistic regression, the risk for DM significantly increased across quartiles of FMI in men aged ≥70. Meanwhile, MMI showed a protective association with DM in men of the same age. The odds ratios (ORs) for the highest quartile versus the lowest quartile of FMI and MMI were 3.116 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.405 to 6.914) and 0.295 (95% CI, 0.157 to 0.554), respectively. In women, the ORs of DM was significantly different across FMI quartiles in those over age 50. The highest quartile of FMI exhibited increased ORs of DM in subjects aged 50 to 69 (OR, 1.891; 95% CI, 1.229 to 2.908) and ≥70 (OR, 2.275; 95% CI, 1.103 to 4.69) compared to lowest quartile. However, MMI was not significantly associated with DM in women of all age groups.
Conclusion Both FMI and MMI were independent risk factors for DM in men aged 70 years or more. In women over 50 years, FMI was independently associated with DM. There was no significant association between MMI and DM in women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research Progress on Correlation between Body Composition Changes and Disease Pro-gression of Type 2 Diabetes
敏 张
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2024; 14(03): 936. CrossRef - Low Skeletal Muscle Mass Accompanied by Abdominal Obesity Additively Increases the Risk of Incident Type 2 Diabetes
Ji Eun Jun, Seung-Eun Lee, You-Bin Lee, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hwan Jee, Jae Hyeon Kim
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 108(5): 1173. CrossRef - Is imaging-based muscle quantity associated with risk of diabetes? A meta-analysis of cohort studies
Shanhu Qiu, Xue Cai, Yang Yuan, Bo Xie, Zilin Sun, Tongzhi Wu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 189: 109939. CrossRef - Whole and segmental body composition changes during mid-follicular and mid-luteal phases of the menstrual cycle in recreationally active young women
Şükran Nazan Koşar, Yasemin Güzel, Mehmet Gören Köse, Ayşe Kin İşler, Tahir Hazır
Annals of Human Biology.2022; 49(2): 124. CrossRef - Body Composition and Diabetes
Hye Jin Yoo
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2021; 22(4): 238. CrossRef
- Research Progress on Correlation between Body Composition Changes and Disease Pro-gression of Type 2 Diabetes
- Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
- Proportion and Characteristics of the Subjects with Low Muscle Mass and Abdominal Obesity among the Newly Diagnosed and Drug-Naïve Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
- Jung A Kim, Soon Young Hwang, Hye Soo Chung, Nam Hoon Kim, Ji A Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Hye Jin Yoo
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(1):105-113. Published online September 28, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0036
- 4,888 View
- 70 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Sarcopenic obesity (SO) is a serious public health concern, few studies have examined the clinical implications of SO in newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients. We evaluated the prevalence of the newly diagnosed, drug-naïve T2DM patients with low muscle mass with abdominal obesity and its association with insulin resistance and other diabetic complications.
Methods We classified 233 drug-naïve T2DM subjects into four groups according to abdominal obesity (waist circumference ≥90 cm in men and ≥85 cm in women) and low muscle mass status (appendicular skeletal muscle <7.0 kg/m2 for men and <5.4 kg/m2 for women).
Results The proportion of the subjects with low muscle mass and abdominal obesity among the newly diagnosed, drug-naïve T2DM patients was 8.2%. Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) increased linearly according to body composition group from normal to abdominal obesity to both low muscle mass and abdominal obesity. The multiple logistic regression analysis indicated that subjects with low muscle mass and abdominal obesity (odds ratio [OR], 9.39; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.41 to 36.56) showed a higher risk for insulin resistance, defined as HOMA-IR ≥3, than those with abdominal obesity (OR, 5.36; 95% CI, 2.46 to 11.69), even after adjusting for other covariates. However, there were no differences in lipid profiles, microalbuminuria, or various surrogate markers for atherosclerosis among the four groups.
Conclusion Subjects with both low muscle mass and abdominal obesity had a higher risk of insulin resistance than those with low muscle mass or abdominal obesity only.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical observation on acupuncture for 80 patients with abdominal obesity in Germany: based on the theory of unblocking and regulating the Belt Vessel
Yuanyuan Li, Hang Xiong, Shuhui Ma, Jingzhang Dai
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science.2023; 21(2): 137. CrossRef - Waist circumference and end‐stage renal disease based on glycaemic status: National Health Insurance Service data 2009–2018
Yun Kyung Cho, Ji Hye Huh, Shinje Moon, Yoon Jung Kim, Yang‐Hyun Kim, Kyung‐do Han, Jun Goo Kang, Seong Jin Lee, Sung‐Hee Ihm
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2023; 14(1): 585. CrossRef - Incidence of sarcopenic obesity in older patients with diabetes and association between sarcopenic obesity and higher-level functional capacity: evaluation based on a consensus statement
Satoshi Ida, Ryutaro Kaneko, Kanako Imataka, Kaoru Okubo, Kentaro Azuma, Kazuya Murata
Endocrine Journal.2023; 70(6): 591. CrossRef - A Novel Anthropometric Parameter, Weight-Adjusted Waist Index Represents Sarcopenic Obesity in Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Min Jeong Park, Soon Young Hwang, Nam Hoon Kim, Sin Gon Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Hye Jin Yoo
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(2): 130. CrossRef - Prevalence of sarcopenic obesity in patients with diabetes and adverse outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Yuan-yuan Zhou, Jin-feng Wang, Qian Yao, Qiu-feng Jian, Zhi-peng Luo
Clinical Nutrition ESPEN.2023; 58: 128. CrossRef - The Correlation Between Leg Muscle Mass Index and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Menggege Liu, Qing Zhang, Juan Liu, Huiling Bai, Ping Yang, Xinhua Ye, Xiaoqing Yuan
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 4169. CrossRef - Sarcopenic Obesity with Normal Body Size May Have Higher Insulin Resistance in Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Tingting Han, Ting Yuan, Xinyue Liang, Ningxin Chen, Jia Song, Xin Zhao, Yurong Weng, Yaomin Hu
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 1197. CrossRef - Relationship between Visceral Adipose Index, Lipid Accumulation Product and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
停停 陈
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2022; 12(04): 3350. CrossRef - Assessment of the relationship between prediabetes and low skeletal mass based on blood creatinine level
S. I. Ibragimova, G. O. Nuskabayeva, Z. N. Shalkharova, K. Zh. Sadykova, G. A. Junusbekova, M. Oran
Diabetes mellitus.2022; 25(3): 226. CrossRef - Changes in body composition and low blood urea nitrogen level related to an increase in the prevalence of fatty liver over 20 years: A cross‐sectional study
Yasushi Imamura, Seiichi Mawatari, Kohei Oda, Kotaro Kumagai, Yasunari Hiramine, Akiko Saishoji, Atsuko Kakihara, Mai Nakahara, Manei Oku, Kaori Hosoyamada, Shuji Kanmura, Akihiro Moriuchi, Hironori Miyahara, Akio ido
Hepatology Research.2021; 51(5): 570. CrossRef - Body Composition and Diabetes
Hye Jin Yoo
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2021; 22(4): 238. CrossRef - Reduced Skeletal Muscle Volume and Increased Skeletal Muscle Fat Deposition Characterize Diabetes in Individuals after Pancreatitis: A Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study
Andre E. Modesto, Juyeon Ko, Charlotte E. Stuart, Sakina H. Bharmal, Jaelim Cho, Maxim S. Petrov
Diseases.2020; 8(3): 25. CrossRef - Low alanine aminotransferase levels predict low muscle strength in older patients with diabetes: A nationwide cross‐sectional study in Korea
Seung Min Chung, Jun Sung Moon, Ji Sung Yoon, Kyu Chang Won, Hyoung Woo Lee
Geriatrics & Gerontology International.2020; 20(4): 271. CrossRef - Association between sarcopenic obesity and higher risk of type 2 diabetes in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Dima Khadra, Leila Itani, Hana Tannir, Dima Kreidieh, Dana El Masri, Marwan El Ghoch
World Journal of Diabetes.2019; 10(5): 311. CrossRef
- Clinical observation on acupuncture for 80 patients with abdominal obesity in Germany: based on the theory of unblocking and regulating the Belt Vessel
- Hepatokines as a Link between Obesity and Cardiovascular Diseases
- Hye Jin Yoo, Kyung Mook Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2015;39(1):10-15. Published online February 16, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.1.10
- 4,616 View
- 53 Download
- 67 Web of Science
- 69 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, which is considered a hepatic manifestation of metabolic syndrome, independently increases the risks of developing cardiovascular disease (CVD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Recent emerging evidence suggests that a group of predominantly liver-derived proteins called hepatokines directly affect the progression of atherosclerosis by modulating endothelial dysfunction and infiltration of inflammatory cells into vessel walls. Here, we summarize the role of the representative hepatokines fibroblast growth factor 21, fetuin-A, and selenoprotein P in the progression of CVD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Overview of the Association Between Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Hypertension
Niki S. Kakouri, Costas G. Thomopoulos, Eirini P. Siafi, Angeliki E. Valatsou, Kyriakos S. Dimitriadis, Iliana P. Mani, Sotirios P. Patsilinakos, Dimitrios M. Tousoulis, Konstantinos P. Tsioufis
Cardiology Discovery.2024; 4(1): 30. CrossRef - The liver-heart axis in patients with severe obesity: The association between liver fibrosis and chronic myocardial injury may be explained by shared risk factors of cardiovascular disease
J. Young, K.A. Seeberg, K.M. Aakre, H. Borgeraas, N. Nordstrand, T. Wisløff, J. Hjelmesæth, T. Omland, J.K. Hertel
Clinical Biochemistry.2024; 123: 110688. CrossRef - From Beats to Metabolism: the Heart at the Core of Interorgan Metabolic Cross Talk
Rafael Romero-Becera, Ayelén M. Santamans, Alba C. Arcones, Guadalupe Sabio
Physiology.2024; 39(2): 98. CrossRef - Exerkines and cardiometabolic benefits of exercise: from bench to clinic
Leigang Jin, Candela Diaz-Canestro, Yu Wang, Michael Andrew Tse, Aimin Xu
EMBO Molecular Medicine.2024; 16(3): 432. CrossRef - Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and left ventricular diastolic dysfunction: A 7-year retrospective cohort study of 3,380 adults using serial echocardiography
Gyuri Kim, Tae Yang Yu, Jae Hwan Jee, Ji Cheol Bae, Mira Kang, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism.2024; 50(3): 101534. CrossRef - Mechanisms underlying the bidirectional association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and hypertension
Hironori Nakagami
Hypertension Research.2023; 46(2): 539. CrossRef - Effects of treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease on heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
Zifeng Yang, Ruifeng Tian, Xiao-Jing Zhang, Jingjing Cai, Zhi-Gang She, Hongliang Li
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - “Alphabet” Selenoproteins: Implications in Pathology
Carmen Beatrice Dogaru, Carmen Duță, Corina Muscurel, Irina Stoian
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(20): 15344. CrossRef - Reversal of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease among Korean
Yun Hwan Oh, Seogsong Jeong, Sun Jae Park, Joseph C Ahn, Sang Min Park
Medicine.2023; 102(44): e35804. CrossRef - Change of cardiovascular risk associated serologic biomarkers after gastric bypass: A comparison of diabetic and non-diabetic Asian patients
Jih-Hua Wei, Ming-Hsien Lee, Wei-Jei Lee, Shu-Chun Chen, Owaid M. Almalki, Jung-Chien Chen, Chun-Chi Wu, Yi-Chih Lee
Asian Journal of Surgery.2022; 45(11): 2253. CrossRef - The effect of 12 weeks of training in water on serum levels of SIRT1 and FGF-21, glycemic index, and lipid profile in patients with type 2 diabetes
Bahram Jamali Gharakhanlou, Solmaz Babaei Bonab
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2022; 42(4): 727. CrossRef - Obesity is an important determinant of severity in newly defined metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease
Ji Hye Huh, Kwang Joon Kim, Seung Up Kim, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International.2022; 21(3): 241. CrossRef - Hepatic PTEN Signaling Regulates Systemic Metabolic Homeostasis through Hepatokines-Mediated Liver-to-Peripheral Organs Crosstalk
Flavien Berthou, Cyril Sobolewski, Daniel Abegg, Margot Fournier, Christine Maeder, Dobrochna Dolicka, Marta Correia de Sousa, Alexander Adibekian, Michelangelo Foti
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(7): 3959. CrossRef - AMP activated kinase negatively regulates hepatic Fetuin-A via p38 MAPK-C/EBPβ/E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Signaling pathway
Vishal Kothari, Jeganathan Ramesh Babu, Suresh T. Mathews, Regis Moreau
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(5): e0266472. CrossRef - Modern aspects of pathogenesis of comorbidity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and hypertension in the presence or absence of chronic kidney disease.
K.O. Prosolenko, К.A. Lapshyna, V.V. Ryabuha
Shidnoevropejskij zurnal vnutrisnoi ta simejnoi medicini.2022; 2022(1): 55. CrossRef - A coagulation factor moonlights in the heart
Dan Tong, Joseph A. Hill
Science.2022; 377(6613): 1382. CrossRef - Fetuin-A and Its Association with Anthropometric, Atherogenic, and Biochemical Parameters and Indices among Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Karolina Kulik-Kupka, Marzena Jabczyk, Justyna Nowak, Paweł Jagielski, Bartosz Hudzik, Barbara Zubelewicz-Szkodzińska
Nutrients.2022; 14(19): 4034. CrossRef - Mitochondrial Dysfunction is a Key Pathway that Links Saturated Fat Intake to the Development and Progression of NAFLD
Ruth C. R. Meex, Ellen E. Blaak
Molecular Nutrition & Food Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - New Insights Into the Comorbidity of Coronary Heart Disease and Depression
Yeshun Wu, Bin Zhu, Zijun Chen, Jiahao Duan, Ailin Luo, Ling Yang, Chun Yang
Current Problems in Cardiology.2021; 46(3): 100413. CrossRef - Liver hepatokines and peroxisomes as therapeutic targets for cardiovascular diseases
Kerui Huang, Hua Bai
Future Cardiology.2021; 17(4): 535. CrossRef - Hepatocardiac or Cardiohepatic Interaction: From Traditional Chinese Medicine to Western Medicine
Yaxing Zhang, Xian-Ming Fang, Michał Tomczyk
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Mitochondria as Players and Targets of Therapies?
Agostino Di Ciaula, Salvatore Passarella, Harshitha Shanmugam, Marica Noviello, Leonilde Bonfrate, David Q.-H. Wang, Piero Portincasa
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(10): 5375. CrossRef - Investigating Fetuin-A and Paraoxonase-1 Activity as Markers in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Based on Body Mass Index: A Prospective Case-Control Study
Tugba Gurbuz, Sebnem Alanya Tosun, Aysegul Cebi, Oya Gokmen, Murat Usta
Cureus.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Extent and features of liver steatosis in vitro pave the way to endothelial dysfunction without physical cell-to-cell contact
Francesca Baldini, Mohamad Khalil, Nadia Serale, Adriana Voci, Piero Portincasa, Laura Vergani
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2021; 31(12): 3522. CrossRef - Association of Fetuin-B with Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Obese Chinese Adults
Zhibin Li, Chunmei He, Yongwen Liu, Dongmei Wang, Mingzhu Lin, Changqin Liu, Xiulin Shi, Zheng Chen, Xuejun Li, Shuyu Yang, Weihua Li
Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis.2020; 27(5): 418. CrossRef - Serum Fetuin-A levels are increased and associated with insulin resistance in women with polycystic ovary syndrome
Sha Liu, Wenjing Hu, Yirui He, Ling Li, Hua Liu, Lin Gao, Gangyi Yang, Xin Liao
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The intrinsic and extrinsic elements regulating inflammation
M. Mollaei, A. Abbasi, Z.M. Hassan, N. Pakravan
Life Sciences.2020; 260: 118258. CrossRef - A Close Relationship between Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Marker and New-Onset Hypertension in Healthy Korean Adults
Jae-Hyung Roh, Jae-Hyeong Park, Hanbyul Lee, Yong-Hoon Yoon, Minsu Kim, Yong-Giun Kim, Gyung-Min Park, Jae-Hwan Lee, In-Whan Seong
Korean Circulation Journal.2020; 50(8): 695. CrossRef - Elevated blood pressure, cardiometabolic risk and target organ damage in youth with overweight and obesity
Procolo Di Bonito, Lucia Pacifico, Maria Rosaria Licenziati, Claudio Maffeis, Anita Morandi, Melania Manco, Emanuele Miraglia del Giudice, Anna Di Sessa, Giuseppina Campana, Nicola Moio, Marco Giorgio Baroni, Claudio Chiesa, Giovanni De Simone, Giuliana V
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2020; 30(10): 1840. CrossRef - Liver governs adipose remodelling via extracellular vesicles in response to lipid overload
Yue Zhao, Meng-Fei Zhao, Shan Jiang, Jing Wu, Jia Liu, Xian-Wen Yuan, Di Shen, Jing-Zi Zhang, Nan Zhou, Jian He, Lei Fang, Xi-Tai Sun, Bin Xue, Chao-Jun Li
Nature Communications.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic Inflammation—A Role for Hepatic Inflammatory Pathways as Drivers of Comorbidities in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease?
Nadine Gehrke, Jörn M. Schattenberg
Gastroenterology.2020; 158(7): 1929. CrossRef - Effect of Moderate Aerobic Exercise on Serum Levels of FGF21 and Fetuin A in Women with Type 2 Diabetes
Exir Vizvari, Parvin farzanegi, Hajar Abbas Zade
Medical Laboratory Journal.2020; 14(6): 17. CrossRef - Fibroblast growth factor 21: A role in cardiometabolic disorders and cardiovascular risk prediction?
Niki Katsiki, Christos Mantzoros
Metabolism.2019; 93: iii. CrossRef - Current and Future Nutritional Strategies to Modulate Inflammatory Dynamics in Metabolic Disorders
Willem van den Brink, Jolanda van Bilsen, Kanita Salic, Femke P. M. Hoevenaars, Lars Verschuren, Robert Kleemann, Jildau Bouwman, Gabriele V. Ronnett, Ben van Ommen, Suzan Wopereis
Frontiers in Nutrition.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Fetuin-A is also an adipokine
Ishwarlal Jialal, Roma Pahwa
Lipids in Health and Disease.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Fibroblast growth factor 21 in lipid metabolism and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Xin Su, Yi Kong, Daoquan Peng
Clinica Chimica Acta.2019; 498: 30. CrossRef - Inter-organ cross-talk in metabolic syndrome
Christina Priest, Peter Tontonoz
Nature Metabolism.2019; 1(12): 1177. CrossRef - The persistence of fatty liver has a differential impact on the development of diabetes: The Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
Ji Cheol Bae, Ji Min Han, Jung Hwan Cho, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sam Kwon, Sung-Woo Park, Eun Jung Rhee
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2018; 135: 1. CrossRef - Hypertension, diabetes, atherosclerosis and NASH: Cause or consequence?
Amedeo Lonardo, Fabio Nascimbeni, Alessandro Mantovani, Giovanni Targher
Journal of Hepatology.2018; 68(2): 335. CrossRef - Frequency and Antibiotic Resistance Pattern of Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli (DEC) Strains Isolated from Children Aged Less Than 10 Years
Shahram Shahraki Zahedani, Nasrin sayadzai
Medical Laboratory Journal .2018; 12(2): 7. CrossRef - Fetuin-A levels are increased in the adipose tissue of diabetic obese humans but not in circulation
Abdelkrim Khadir, Sina Kavalakatt, Dhanya Madhu, Maha Hammad, Sriraman Devarajan, Jaakko Tuomilehto, Ali Tiss
Lipids in Health and Disease.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Implication of liver enzymes on incident cardiovascular diseases and mortality: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Kyung Mook Choi, Kyungdo Han, Sanghyun Park, Hye Soo Chung, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji-A Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, Yong Gyu Park, Seon Mee Kim
Scientific Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Obesity and Male Infertility: Role of Fatty Acids in the Modulation of Sperm Energetic Metabolism
Alessandra Ferramosca, Mariangela Di Giacomo, Natalina Moscatelli, Vincenzo Zara
European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - The association between circulating fetuin-A levels and type 2 diabetes mellitus risk: systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
F. Roshanzamir, M. Miraghajani, M. H. Rouhani, M. Mansourian, R. Ghiasvand, S. M. Safavi
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2018; 41(1): 33. CrossRef - Clinical and Body Compositional Factors Associated with Metabolic Syndrome in Obese Koreans: A Cross-Sectional Study
Yoo Mee Kim, Sunghoon Kim, Se Hwa Kim, Young Jun Won
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2018; 16(6): 290. CrossRef - Association of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis with subclinical myocardial dysfunction in non-cirrhotic patients
Yong-ho Lee, Kwang Joon Kim, Myung eun Yoo, Gyuri Kim, Hye-jin Yoon, Kwanhyeong Jo, Jong-Chan Youn, Mijin Yun, Jun Yong Park, Chi Young Shim, Byung-Wan Lee, Seok-Min Kang, Jong-Won Ha, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun Seok Kang
Journal of Hepatology.2018; 68(4): 764. CrossRef - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and hypertension: coprevalent or correlated?
Dimitrios Oikonomou, Georgios Georgiopoulos, Vassiliki Katsi, Chris Kourek, Constantinos Tsioufis, Alexendra Alexopoulou, Evaggelia Koutli, Dimitrios Tousoulis
European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2018; 30(9): 979. CrossRef - Implication of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Metabolic Syndrome, and Subclinical Inflammation on Mild Renal Insufficiency
Ga Eun Nam, Soon Young Hwang, Hye Soo Chung, Ju Hee Choi, Hyun Jung Lee, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji-A Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyung Mook Choi
International Journal of Endocrinology.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - Serum levels of fetuin-A are negatively associated with log transformation levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone in patients with hyperthyroidism or euthyroidism
Fen-Yu Tseng, Yen-Ting Chen, Yu-Chiao Chi, Pei-Lung Chen, Wei-Shiung Yang
Medicine.2018; 97(46): e13254. CrossRef - Relationship of Circulating Fetuin-A Levels with Body Size and Metabolic Phenotypes
Hye Soo Chung, Hyun Jung Lee, Soon Young Hwang, Ju-Hee Choi, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A. Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Dong Seop Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyung Mook Choi
International Journal of Endocrinology.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - Lobeglitazone, a Novel Thiazolidinedione, Improves Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Type 2 Diabetes: Its Efficacy and Predictive Factors Related to Responsiveness
Yong-ho Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim, So Ra Kim, Heung Yong Jin, Eun-Jung Rhee, Young Min Cho, Byung-Wan Lee
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2017; 32(1): 60. CrossRef - Dietary fatty acids influence sperm quality and function
A. Ferramosca, N. Moscatelli, M. Di Giacomo, V. Zara
Andrology.2017; 5(3): 423. CrossRef - Obesity is more closely related with hepatic steatosis and fibrosis measured by transient elastography than metabolic health status
Ji Hye Huh, Kwang Joon Kim, Seung Up Kim, Seung Hwan Han, Kwang-Hyub Han, Bong-Soo Cha, Choon Hee Chung, Byung-Wan Lee
Metabolism.2017; 66: 23. CrossRef - Hepatokines: linking nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance
Ruth C. R. Meex, Matthew J. Watt
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2017; 13(9): 509. CrossRef - Association of leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin 2 (LECT2) with NAFLD, metabolic syndrome, and atherosclerosis
Hye Jin Yoo, Soon Young Hwang, Ju-Hee Choi, Hyun Jung Lee, Hye Soo Chung, Ji-A Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, Dong Seop Choi, Kyung Mook Choi, Pavel Strnad
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(4): e0174717. CrossRef - T2DiACoD: A Gene Atlas of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Associated Complex Disorders
Jyoti Rani, Inna Mittal, Atreyi Pramanik, Namita Singh, Namita Dube, Smriti Sharma, Bhanwar Lal Puniya, Muthukurussi Varieth Raghunandanan, Ahmed Mobeen, Srinivasan Ramachandran
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - The fatty liver index as a predictor of incident chronic kidney disease in a 10-year prospective cohort study
Ji Hye Huh, Jang Young Kim, Eunhee Choi, Jae Seok Kim, Yoosoo Chang, Ki-Chul Sung, Tatsuo Shimosawa
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(7): e0180951. CrossRef - A high‐fat diet negatively affects rat sperm mitochondrial respiration
A. Ferramosca, A. Conte, N. Moscatelli, V. Zara
Andrology.2016; 4(3): 520. CrossRef - The Impact of Organokines on Insulin Resistance, Inflammation, and Atherosclerosis
Kyung Mook Choi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(1): 1. CrossRef - Metformin Restores Parkin-Mediated Mitophagy, Suppressed by Cytosolic p53
Young Song, Woo Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Eun Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2016; 17(1): 122. CrossRef - Pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
Wensheng Liu, Robert D. Baker, Tavleen Bhatia, Lixin Zhu, Susan S. Baker
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences.2016; 73(10): 1969. CrossRef - The ratio of skeletal muscle mass to visceral fat area is a main determinant linking circulating irisin to metabolic phenotype
You-Cheol Hwang, Won Seon Jeon, Cheol-Young Park, Byung-Soo Youn
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Sirtuin 3 (SIRT3) Regulates α-Smooth Muscle Actin (α-SMA) Production through the Succinate Dehydrogenase-G Protein-coupled Receptor 91 (GPR91) Pathway in Hepatic Stellate Cells
Ying Hui Li, Dae Hee Choi, Eun Hye Lee, Su Ryeon Seo, Seungkoo Lee, Eun-Hee Cho
Journal of Biological Chemistry.2016; 291(19): 10277. CrossRef - Statins Increase Mitochondrial and Peroxisomal Fatty Acid Oxidation in the Liver and Prevent Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis in Mice
Han-Sol Park, Jung Eun Jang, Myoung Seok Ko, Sung Hoon Woo, Bum Joong Kim, Hyun Sik Kim, Hye Sun Park, In-Sun Park, Eun Hee Koh, Ki-Up Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2016; 40(5): 376. CrossRef - Hormetic and regulatory effects of lipid peroxidation mediators in pancreatic beta cells
Giuseppe Maulucci, Bareket Daniel, Ofir Cohen, Yossef Avrahami, Shlomo Sasson
Molecular Aspects of Medicine.2016; 49: 49. CrossRef - Extrahepatic Complications of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Kristina R. Chacko, John Reinus
Clinics in Liver Disease.2016; 20(2): 387. CrossRef - Use of a Diabetes Self-Assessment Score to Predict Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
Gyuri Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Young Min Park, Jungghi Kim, Heesuk Kim, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee, Dae Jung Kim
Medicine.2015; 94(27): e1103. CrossRef - A Prospective Study of Fatty Liver Index and Incident Hypertension: The KoGES-ARIRANG Study
Ji Hye Huh, Song Vogue Ahn, Sang Baek Koh, Eunhee Choi, Jang Young Kim, Ki-Chul Sung, Eung Ju Kim, Jeong Bae Park, Vincent Wong
PLOS ONE.2015; 10(11): e0143560. CrossRef - Endocrine causes of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Laura Marino
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2015; 21(39): 11053. CrossRef
- Overview of the Association Between Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Hypertension
- Adipose Gene Expression Profiles Related to Metabolic Syndrome Using Microarray Analyses in Two Different Models
- Hye Jin Yoo, Hwan-Jin Hwang, Tae Woo Jung, Ja Young Ryu, Ho Cheol Hong, Hae Yoon Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyung Mook Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2014;38(5):356-365. Published online October 17, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2014.38.5.356
- 4,192 View
- 43 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPAR-γ) agonist has a wide-ranging influence on multiple components of metabolic syndrome. The Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) rat is a useful animal model of metabolic syndrome. To determine genes related to metabolic syndrome, we examined overlapping genes that are simultaneously decreased by PPAR-γ agonists and increased in OLETF rats using microarrays in two different models.
Methods In the first microarray analysis, PPAR-γ agonist-treated
db/db mice were compared to standard diet-feddb/db mice. In the second microarray analysis, OLETF rats were compared to Long-Evans Tokushima Otsuka (LETO) rats (control of OLETF rats).Results Among the overlapping genes, in the present study, we validated that lipocalin-2 expression was significantly decreased in the visceral adipose tissue of PPAR-γ agonist-treated
db/db mice compared to standard diet-feddb/db mice and increased in OLETF rats compared to LETO rats using real time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. Furthermore, we showed for the first time that lipocalin-2 expression was significantly increased in the visceral adipose tissues of obese humans compared with nonobese humans. In addition, the expression level of lipocalin-2 in human visceral adipose tissue had a significant positive correlation with body mass index, serum interleukin-6, adipocyte fatty acid binding protein levels, and white blood cell count.Conclusion Lipocalin-2 was confirmed to be a significant adipokine affected by PPAR-γ agonist and obesity in the present study. Also, for the first time in human visceral adipose tissue, it was determined that the expression of lipocalin-2 from obese humans was significantly increased and correlated with circulating inflammatory markers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Lipocalin‐2—The myth of its expression and function
Dahui Li, Wai Yan Sun, Bowen Fu, Aimin Xu, Yu Wang
Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology.2020; 127(2): 142. CrossRef - Lipocalin-2 counteracts metabolic dysregulation in obesity and diabetes
Ioanna Mosialou, Steven Shikhel, Na Luo, Peristera Ioanna Petropoulou, Konstantinos Panitsas, Brygida Bisikirska, Nyanza J. Rothman, Roxane Tenta, Bertrand Cariou, Matthieu Wargny, Elisabeth Sornay-Rendu, Thomas Nickolas, Mishaela Rubin, Cyrille B. Confav
Journal of Experimental Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolism and adult neurogenesis: Towards an understanding of the role of lipocalin-2 and iron-related oxidative stress
Ana Catarina Ferreira, Nuno Sousa, João M. Bessa, João Carlos Sousa, Fernanda Marques
Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews.2018; 95: 73. CrossRef - LH-21, A Peripheral Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Antagonist, Exerts Favorable Metabolic Modulation Including Antihypertensive Effect in KKAy Mice by Regulating Inflammatory Cytokines and Adipokines on Adipose Tissue
Ziqi Dong, Hui Gong, Yadan Chen, Hong Wu, Jun Wu, Yinghong Deng, Xinmao Song
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Lipocalin 2 produces insulin resistance and can be upregulated by glucocorticoids in human adipose tissue
Prasad G. Kamble, Maria J. Pereira, Cherno O. Sidibeh, Sam Amini, Magnus Sundbom, Joey Lau Börjesson, Jan W. Eriksson
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2016; 427: 124. CrossRef - Serum lipocalin-2 levels are positively associated with not only total body fat but also visceral fat area in Chinese men
Yuqi Luo, Xiaojing Ma, Xiaoping Pan, Yiting Xu, Qin Xiong, Yunfeng Xiao, Yuqian Bao, Weiping Jia
Medicine.2016; 95(30): e4039. CrossRef - From the periphery to the brain: Lipocalin-2, a friend or foe?
Ana C. Ferreira, Sandro Dá Mesquita, João C. Sousa, Margarida Correia-Neves, Nuno Sousa, Joana A. Palha, Fernanda Marques
Progress in Neurobiology.2015; 131: 120. CrossRef
- Lipocalin‐2—The myth of its expression and function
- Safety and Efficacy of Modern Insulin Analogues
- Hye Jin Yoo, Keun Yong Park, Kang Seo Park, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Kyung Wan Min, Jeong Hyun Park, Sang Ah Chang, Bong Soo Cha, Dong-Jun Kim, Yong Seong Kim, Tae Keun Oh, Suk Chon, Il Seong Nam-Goong, Mi Jin Kim, Hye-Soon Kim, Young Sik Choi, You Hern Ahn, Sora Lee, Sei Hyun Baik
- Diabetes Metab J. 2013;37(3):181-189. Published online June 14, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.3.181
- 4,113 View
- 32 Download
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background A1chieve® was a noninterventional study evaluating the clinical safety and efficacy of biphasic insulin aspart 30, insulin detemir, and insulin aspart.
Methods Korean type 2 diabetes patients who have not been treated with the study insulin or have started it within 4 weeks before enrollment were eligible for the study. The patient selection and the choice of regimen were at the discretion of the physician. The safety and efficacy information was collected from the subjects at baseline, week 12, and week 24. The number of serious adverse drug reactions (SADRs) was the primary endpoint. The changes of clinical diabetic markers at week 12 and/or at week 24 compared to baseline were the secondary endpoints.
Results Out of 4,058 exposed patients, 3,003 completed the study. During the study period, three SADRs were reported in three patients (0.1%). No major hypoglycemic episodes were observed and the rate of minor hypoglycemic episodes marginally decreased during 24 weeks (from 2.77 to 2.42 events per patient-year). The overall quality of life score improved (from 66.7±15.9 to 72.5±13.5) while the mean body weight was slightly increased (0.6±3.0 kg). The 24-week reductions in glycated hemoglobin, fasting plasma glucose and postprandial plasma glucose were 1.6%±2.2%, 2.5±4.7 mmol/L, and 4.0±6.4 mmol/L, respectively.
Conclusion The studied regimens showed improvements in glycemic control with low incidence of SADRs, including no incidence of major hypoglycemic episodes in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Insulin therapy for adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a position statement of the Korean Diabetes Association, 2017
Byung-Wan Lee, Jin Hwa Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyu Yeon Hur, Nan-Hee Kim, Sang Youl Rhee, Hyun Jin Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Seok-O Park, Kyung Mook Choi
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2017; 32(6): 967. CrossRef - Insulin Therapy for Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association, 2017
Byung-Wan Lee, Jin Hwa Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyu-Yeon Hur, Nan-Hee Kim, Sang Youl Rhee, Hyun Jin Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Seok-O Park, Kyung Mook Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(5): 367. CrossRef - An information and communication technology-based centralized clinical trial to determine the efficacy and safety of insulin dose adjustment education based on a smartphone personal health record application: a randomized controlled trial
Gyuri Kim, Ji Cheol Bae, Byoung Kee Yi, Kyu Yeon Hur, Dong Kyung Chang, Moon-Kyu Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim, Sang-Man Jin
BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Characteristics Predictive for a Successful Switch from Insulin Analogue Therapy to Oral Hypoglycemic Agents in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Gyuri Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee, Byung-Wan Lee
Yonsei Medical Journal.2016; 57(6): 1395. CrossRef - Avoiding or coping with severe hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes
Jae-Seung Yun, Seung-Hyun Ko
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2015; 30(1): 6. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics of Patients Responding to Once-Daily Basal Insulin Therapy in Korean Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes
Sun Ok Song, You-Cheol Hwang, Kyu-Jeung Ahn, Bong Soo Cha, Young Duk Song, Dae Wook Lee, Byung-Wan Lee
Diabetes Therapy.2015; 6(4): 547. CrossRef - The optimal morning:evening ratio in total dose of twice‐daily biphasic insulin analogue in poorly controlled Type 2 diabetes: a 24‐week multi‐centre prospective, randomized controlled, open‐labelled clinical study
C. H. Jung, J.‐Y. Park, J. H. Cho, K.‐H. Yoon, H. K. Yang, Y.‐H. Lee, B. S. Cha, B.‐W. Lee
Diabetic Medicine.2014; 31(1): 68. CrossRef -
The glycemic efficacies of insulin analogue regimens according to baseline glycemic status in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes: sub‐analysis from the A
1
chieve
®
study
Y.‐C. Hwang, J. G. Kang, K. J. Ahn, B. S. Cha, S.‐H. Ihm, S. Lee, M. Kim, B.‐W. Lee
International Journal of Clinical Practice.2014; 68(11): 1338. CrossRef - Letter: Efficacy and Safety of Biphasic Insulin Aspart 30/70 in Type 2 Diabetes Suboptimally Controlled on Oral Antidiabetic Therapy in Korea: A Multicenter, Open-Label, Single-Arm Study (Diabetes Metab J2013;37:117-24)
Byung-Wan Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2013; 37(3): 212. CrossRef
- Insulin therapy for adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a position statement of the Korean Diabetes Association, 2017

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





